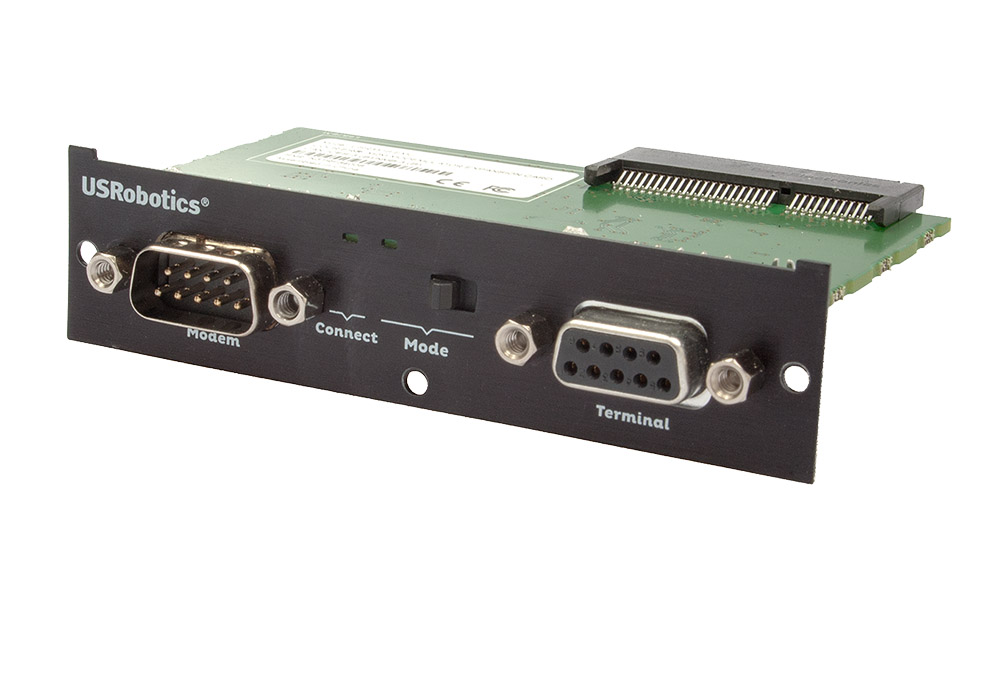
USR3516-EMU
COURIER® MODEMULATOR™ EXPANSION CARD
MODEM EMULATOR EXPANSION CARD FOR M2M CELLULAR GATEWAYS USR3510, USR803510
EASY CONVERSION OF LEGACY DIAL-UP OR LEASED LINE SOLUTIONS TO THE CELLULAR NETWORK
The new USR® Courier® Modemulator™ Expansion Card when installed in the USR M2M Cellular Gateway is a drop-in cellular replacement for legacy analog systems that require peer-to-peer connectivity†. Emulating a dial-up modem allows equipment to seamlessly connect over a cellular network instead of over the PSTN in legacy M2M applications. Existing legacy hardware and software systems remain untouched when used with the Modemulator — providing extended product life and simplified cellular deployments. Compatibility with both the PSTN and packet switched data networks provides network flexibility that allows an open ended transition plan and eliminates the need for a system overhaul — saving both time and money. By providing a 2-in-1 device, analog customers can transition select sites to cellular in the most efficient and cost-effective way while utilizing the network that is right for the situation. USR's Modemulator provides reliable, secure connections for mission critical M2M applications.

When installed in the USR3510 M2M Cellular Gateway the exclusive USR Modemulator provides a simple drop-in cellular replacement for legacy dial-up analog systems that require peer-to-peer connectivity.
AVAILABILITY
AVAILABILITY
Product Code: USR3516-EMU
US Availability: Discontinued
INTERNATIONAL
Canada- Discontinued
Europe- Discontinued
Asia Pacific- Not Available
Latin America- Not Available
For Export Control (ECCN & HTS) please Contact Us for the latest information.
CONTACT USR
FEATURES
MULTIPLE MODES
- Peer-to-Peer mode† provides true drop-in replacement
- Single ended mode for connecting with traditional TCP Client or Server
- Bypass mode for serial gateway operation
- Send commands to the remote Modemulator with remote command mode
SIMPLIFIED CONVERSION
- No need to install middleware or upgrade legacy communications software that expects analog modem & PSTN
- With an optional serial modem, initiate and answer connections over the PSTN to sites with analog modems
- Support for a "mixed network" of both analog and cellular devices allows gradual modem replacement
- Unified interface and protocol for connecting both cellular and analog sites
- Continue to use the USR M2M Cellular Gateway after transition complete
MODEM EMULATION
- Compatible with common Hayes modem AT commands
- Generates modem result codes including RING, RINGING, CONNECT, NO CARRIER, NO DIALTONE, and BUSY
- Outbound and inbound calling
- Supports baud rates from 300 to 115.2k bps
- Peer-to-peer connections
- Stores up to 7,200 phone numbers/IP addresses
- Direct IP dialing
- Emulate leased line operation‡
- RS-232 break signal handling‡
WIRELESS
- When installed in the USR M2M Cellular Gateway (USR3510 or USR803510)
- 3G UMTS or CDMA2000/UMTS *
- 2G GSM or CDMA/GSM *
- Configure locally with intuitive embedded GUI
- Manage remote device's software and configuration with USR Universe - a free cloud application
- Secured internal SIM slot
- Persistent connectivity and auto reboot and recovery
SECURITY & RELIABILITY
- Required private cellular network ensures continued secure connections
- Login banner and security warning banner
- Prompted password access
- Caller ID screening
- Dialback security‡
EASY SETUP
- Fast implementation and deployment in analog based solutions
- Easy configuration using familiar AT commands in the CLI
ADVANCED FEATURES
- Auto-switchover to an attached dial-up modem for PSTN connections
SPECIFICATIONS & STANDARDS
GENERAL
- Expansion card compatible with the primary slot of the USR M2M Cellular Gateway
- Custom USR software for the USR M2M Cellular Gateway
PHYSICAL
- DTE interface: 1 RS-232 DB9 Male connector
- DCE interface: 1 RS-232 DB9 Female connector
- 2 LEDs indicators: system connect status, operating mode
- 1 mode switch: Modemulator/Gateway
SERIAL PORT RATINGS
- Terminal Port RS-232C DCE: Auto-baud detection of 115200, 57600, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, and 300 bps
- Modem Port RS-232C DTE: 115200, 57600, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, and 300 bps
POWER
- 3.3vdc from expansion slot bus
- 149 mW (typical)
DEVICE SECURITY
- Connects over a secure private network
- Support for 1 Administrator account and 9 User accounts
- Password login
- Caller ID screening
- Dialback security‡
- Configurable security warning banner (up to 256 characters)
- Configurable login banner (up to 64 characters)
MINIMUM SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
- Gateway hardware: USR3510 with available primary slot
- Gateway system firmware: version 1.41 or higher (upgrades available)
- Peripheral hardware: RS-232 serial analog modem with access to PTSN
- Cellular device-to-device routing (for peer-to-peer operation
- Computer hardware/software:
- Ethernet port/web browser (for Gateway set-up)
- RS-232 DTE port/terminal software (for Modemulator set-up)
COMMAND LINE INTERFACE
- Compatible with common Hayes modem AT commands
REGULATORY & APPROVALS
- UL/CSA 60950-1
- ICES-003
- CE
- FCC Part 15 Class A
- RoHS Compliant
- REACH
ENVIRONMENTAL
- Temperature conditions: Operating: -30 to 70°ree; C, Non-Operating: -40 to 85°ree; C
- Humidity operational: 5%-95% non-condensing
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS/WEIGHT
- 4.0 x 2.75 x 1.38 in. (10.15 x 6.95 x 3.5 cm)
- .16 lb ( 72.5 g)
PRODUCT DIMENSIONS/WEIGHT
- 3.75 x 2.42 x 0.95 in. (9.52 x 6.15 x 2.41 cm)
- .10 lb ( 45.35 g)
PACKAGE CONTENTS
- USR Courier Modemulator Expansion Card
PRODUCT NUMBERS
- USR3516-EMU
WARRANTY
Two-year limited manufacturer warranty from date of purchase. Click here for full warranty information.
BENEFITS
Modemulator Benefits
- Simplifies the transition from dial-up to cellular
- Extend the life of legacy M2M communications systems
- Drop-in replacement for serial dial-up modems
- Move to cellular M2M with no changes in legacy software or hardware
- Supports mixed cellular/dial-up networks for slow rollouts or ad hoc replacements
- Analog and cellular connections are indistinguishable to legacy software
- The identical procedures for dialing cellular or analog remote network sites provide operational transparency to technicians
Benefits of moving from dial-up to cellular M2M
- Mitigate the decline of phone service availability
- Reduce operating costs of communications systems
Benefits of moving from dial-up to cellular Remote Network Out-of-band Management
- Manage sites where land line service is not available
- Regain control of remote sites connectivity to eliminate nuisance landline disconnections
- Generate additional revenue by including connectivity with management services
- Reduce operating costs of communications systems
- A private cellular network is inherently secure
APPLICATIONS
Modemulator Applications
The USR3516-EMU and USR3520 equipment is specifically engineered for the easy conversion to cellular of legacy systems that use analog serial modems, POTs lines, and legacy communications software including:
- Automation
- ATMs
- Digital Signage
- Home Healthcare
- Point of Sale/Kiosks
- Remote Management
- SCADA
- Security Systems
- Utilities
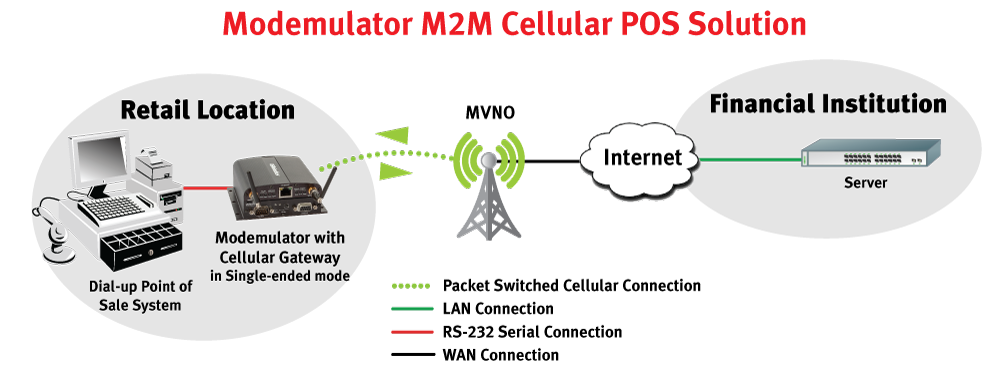
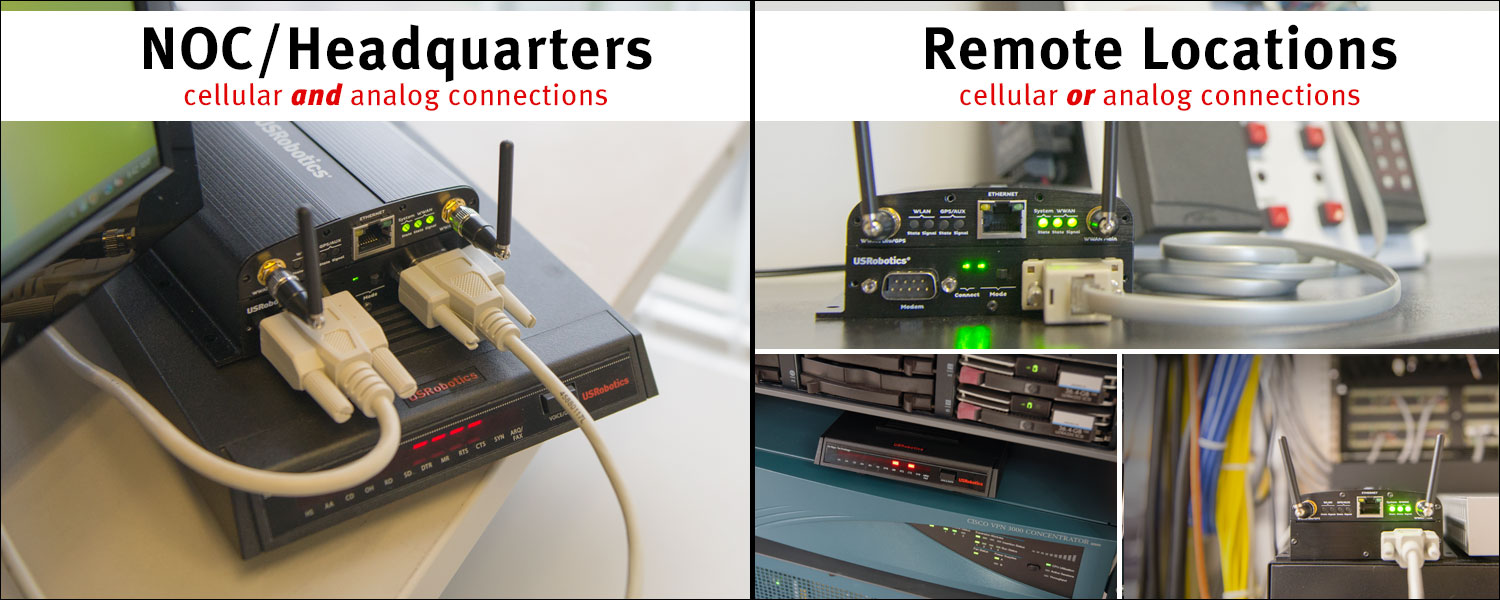
USE CASES
Remote Management
The Challenge
In remote network management applications, Network Managers oversee network infrastructure equipment that is installed at many remote sites. For years, dial-up analog modems have been used to make contact over the PSTN to the remote sites to enable the remote management activities.
As PSTN service becomes less available and more expensive, an upgrade path to cellular remote management is needed. However, the operation of cellular modems and cellular networks are drastically different from the operation of analog modems and legacy telephone networks, making the transition difficult.
The Solution
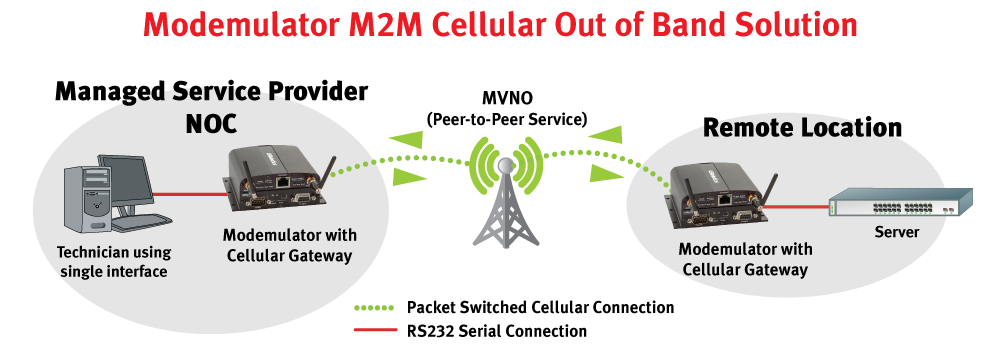
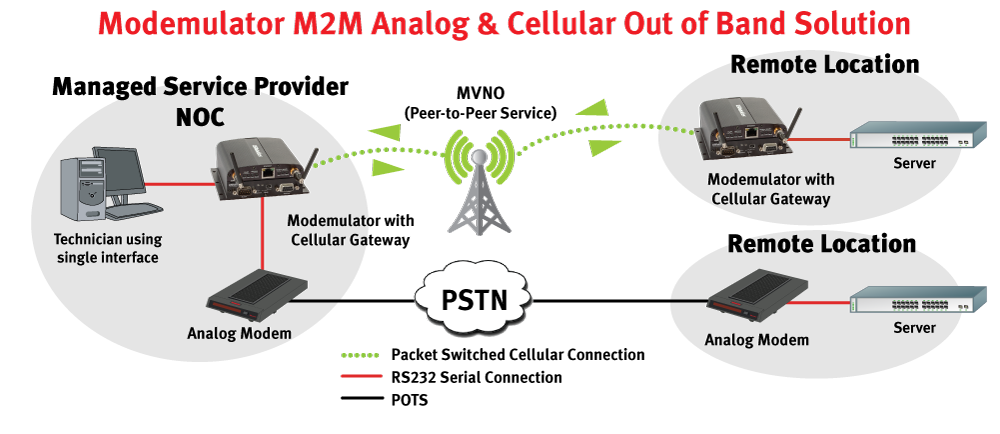
USRobotics has developed a technology called “Modemulation” that can simplify the transition from dial-up out-of-band remote management to cellular. Using a Modemulator at the network operations center, a Network Manager can contact a remote Modemulator over the cellular data network by entering the same dial command that is used for dial-up modems. The two Modemulators replace two dial-up modems and operate as a seamless “drop-in replacement” for dial-up modems and the PSTN.
The Modemulator can also route a connection over the PSTN from a local dial-up modem to a dial-up modem at a remote site that hasn’t been upgraded yet. Both cellular and dial-up sites can be managed conveniently using one terminal and the same familiar dial command.

How It Works
The local Modemulator interfaces to a terminal’s serial port, just as a dial-up modem would. The Modemulator accepts commands and returns responses that mimic a dial-up modem. The remote Modemulator interfaces to the console port of the networking equipment (or port server), just as a dial-up modem would.
An Administrator assigns an arbitrary phone number to each remote Modemulator, and enters that phone number and the IP address and port number of each remote Modemulator into a phonebook in the local Modemulator. When a dial command (e.g. ATDT555-1234) is entered into the Modemulator from the terminal, it searches its phonebook for an associated IP address. If an entry is found, it will connect to the remote Modemulator, allowing the Operator to manage the remote networking equipment.
The connection is made to a GSM or CDMA 3G cellular data network, and the data routing is provided by a Mobile Virtual Network Operator (MVNO). A special service from the MVNO allows routing from one cellular device to another within their network, without crossing a firewall or traversing the public Internet. Such private data routing is extremely secure because 1) cellular data networks do not allow direct device-to-device communication, 2) the subscriber’s private sub-net is isolated from other devices on the MVNO network, and 3) routing from the public Internet is blocked by the MVNO firewall.
If an entry is not found in its phonebook, the Modemulator realizes that the phone number is addressing a dial-up site and automatically routes the dial command to an attached dial-up modem.
FAQs
What is a “Modemulator”?
USR’s exclusive “Modemulator” is an expansion card that when installed in a USR3510/USR803510 Cellular Gateway serves as a drop-in replacement of serial dial-up modems. The Modemulator emulates a dial-up modem, which extends the life of application software and hardware while providing the benefits of cellular connectivity.
The Modemulator is also unique in that it can maintain support of peer-to-peer dial-up connections as well as cellular connections.
Why can’t I use any cellular modem as a drop-in dial-up modem replacement?
Most cellular networks use a different type of technology that isn't compatible with dial-up analog systems. Our Whitepaper explains in detail the how's and why's but the high level answer is that most cellular data networks are packet based, rely on IP addresses, and are client/server whereas dial-up systems are peer-to-peer direct connection and rely on phone numbers which normally cannot communicate without additional hardware and/or software that could complicate how a solution works.
Learn more with the Cellular to Cellular Data Communications White Paper
Why Emulate an Analog Modem & the PSTN?
Legacy M2M application software that uses an analog modem for communications will send commands to the analog modem that set-up the modem and initiate or answer calls. Such software is generally not able to set-up and initiate or answer calls using a cellular data modem or gateway because cellular modem commands, cellular gateway GUI, and the cellular network are fundamentally different than the analog modem commands and phone network.
USR Modemulator technology allows a legacy M2M system to be conveniently converted to cellular without upgrading or replacing application software. The Modemulator accepts and responds to the most common analog modem commands, and sends result codes that mimic a PSTN connection to the application software, which enables drop-in compatibility with the legacy application software.
How much can I expect to save by replacing analog modems with Modemulators?
The cost of analog phone lines is on average $50 per month per line. Cellular services when pooled can provide even greater cost savings with small data packages and low data volumes. The cost savings increase as the volume goes up, whereas the dial-up monthly expenses are consistent but pricey.
Can I replace leased line analog modems with Modemulators?
With firmware release 1.0.02, leased line dial-up modems can be replaced and provide even greater cost savings per month.
Can I use the SIM from my phone for Modemulator?
Generally no. The SIM from your phone is not provisioned for peer-to-peer data connectivity, which Modemulators require in order to emulate the analog PSTN and dial-up modems. However, depending on how your SIM is provisioned, it may allow connectivity to the Internet, and Modemulator can use this type of connectivity when operating in single-ended mode to originate a connection to the IP address of a TCP/IP server.
How does the Modemulator work?
In Modemulator (modem + emulator) mode, the Modemulator presents to a User (or to legacy application software) a command-line interface (CLI) that mimics the AT commands and responses of analog modems, but connects to another Modemulator (or to an IP server) over a cellular data network instead of the public switched telephone network (PSTN). This allows the easy conversion of a legacy M2M system that was based on analog modems connecting over the PSTN to a more modern M2M system connecting over ubiquitous cellular data networks, without upgrading legacy application software that expects an analog modem, or without installing new middleware onto the application computers.
To facilitate the gradual conversion of legacy systems to cellular, the Modemulator can also initiate and answer connections over the PSTN to sites with analog modems by automatically diverting commands to an analog modem attached to its MODEM serial port. This provides the User a unified interface and protocol for connecting with both cellular and analog sites.
Learn more with the Cellular to Cellular Data Communications White Paper
DOCUMENTATION
IMAGES
VIDEO
Understanding Cellular Data Connectivity for M2M
Understanding the Cellular data communication technology differs from legacy dial-up analog connections.
Included are:
Common Misunderstandings 1:05
Making Cellular Work 2:12
Additional Online Documentation 7:37
Length: 8:22 minutes
Introducing the USR Modemulator™
Learn how USR's Modemulator Expansion Card (USR3516-EMU) makes converting from analog to cellular simple and easy.
Length: 1:30 minutes
Intro to the Modemulator Data Communications System
Video explains what a “Modemulator” is, the target applications, how it works and then shows a demonstration of how to configure the Modemulator with a Windows GUI.
Length: 17:41 minutes
Modemulator Expansion Card Installation
How to install a USR Modemulator Expansion Card (USR3516-EMU) into the USR3510/USR803510 Courier® M2M Cellular Gateway and upgrade the firmware to make the unit a USR3520/USR803520 Modemulator.
Length: 6:27 minutes
Modemulator Instructional Video #1 - Using Manual Answer or Auto-Answer
How to configure the USR3516-EMU/USR3520 Cellular Gateway Modemulator to manually answer or to auto answer incoming calls
0:21 Manual Answer Review
0:55 Manual Answer Configuration
2:15 Auto Answer Review
2:44 Auto Answer Configuration
Length: 4:56 minutes
Modemulator Instructional Video #2 - Dialing Phone Numbers or IP Addresses
How to use the dial command or direct dial command to make a cellular connection on the USR3516-EMU/USR3520 Cellular Gateway Modemulator
0:40 Overview
1:10 Using the Dial Command- Setting up the Dialing Directory
2:30 Using the Dial Command - Dialing simulated analog phone numbers
3:30 Using the Dial Command - Dialing real analog phone numbers
4:08 Dialing an IP Address - Using the Direct Dial Command
4:50 Dialing an IP Address - Application
5:15 Summary
Length: 6:43 minutes
Modemulator Instructional Video #3 - Dial Security
Modemulator Instructional Video #3 - How to enable and use the Modemulator's dial security features to prevent unauthorized connections.
0:38 Dial Security Overview
1:51 Caller ID Screening
2:32 Enable Caller ID Screening
4:30 Password Prompting
5:40 Enable Password Prompting
7:00 Using Dialback Security
8:34 Enable Dialback Security
9:55 Summary
Length: 12:08 minutes
Modemulator Instructional Video #4 - Leased Line
Modemulator Instructional Video #4 - How to enable and use the Modemulator's lease line mode so that analog modems used in leased line applications can be replaced by Modemulators.
0:40 Review of Analog Leased Line Operation
1:30 Modemulator Leased Line Operation (always on point to point connection between serial applications)
2:21 Enabling Leased Line Mode
6:53 Summary
Length: 7:51 minutes
Modemulator Instructional Video #5 - Single-ended Operation
How to enable and use the Modemulator's single ended mode for legacy applications that need to connect and interoperate with any TCPIP server or client.
0:44 Review of Normal Modemulator Operation
1:48 Modemulator Single-ended Operation
3:48 Enabling Single-Ended Mode
5:40 Summary
Length: 6:34 minutes
Modemulator Instructional Video #6 - Remote Command Mode
How to manage a remote Modemulator using Remote Command Mode.
0:41 Overview of Remote Command Mode
1:04 Enabling Remote Command Mode
1:49 Using Remote Command Mode
2:53 Exiting a Remote Command Session
3:50 Remote Command Mode with Dial Security
5:54 Update Firmware of a Remote Modemulator
6:39 Summary
Length: 7:21 minutes
Modemulator Instructional Video #7 – Modemulator Firmware Upgrade
Video explains and demonstrates how to upgrade Modemulator to latest firmware.
0:48 Requirements & Setup
2:04 Checking the Modemulator's firmware version
3:00 Getting new firmware (www.usr.com/support/3520)
4:53 Loading the new firmware into the Modemulator
6:28 If the Modemulator remains in boot mode
7:13 Remote firmware upgrade
8:02 Summary
Length: 8:32 minutes
Modemulator GUI Overview
Full overview of the USR5616-EMU/USR3520 USR Modemulator Cellular Gateway Graphical User Interface.
0:26 What is the Modemulator GUI Application?
1:51 Requirements
2:33 Tour of the Configuration Dashboard
10:35 Tour of the Phone Directory
12:54 Tour of the Terminal
15:16 Summary
Length: 15:51 minutes
Referenced Materials:
www.usr.com/support/3520
www.usr.com/support/3516-emu
* Dual radio is not available on USR803510.
† Wireless Master Service, peer-to-peer routing, or device-to-device routing service is required for the peer-to-peer functionality.
‡ Features available on firmware version 1.0.02 and higher. Available for download at www.usr.com/support/3516-emu